Meet the 19-year-old MIT dropout ‘replacing gunpowder’ for the defense industry
By Aria Alamalhodaei– Jul 13, 2023
A version of this article was first published on TechCrunch
Silicon Valley loves its wunderkinds, but the same cannot be said of Washington, D.C., where the central mandate is not to take risks, but to de-risk.
Or that’s how it’s been until recently. The two American power centers have been solidifying a détente, spurred by the war in Ukraine and the great global competition with China. Investor interest in defense startups has grown, with nearly $8 billion of VC dollars flowing to aerospace and defense startups last year — up from just $1.4 billion in 2018, according to the analytics firm PitchBook.
Concurrently, Pentagon leaders have acknowledged that getting startup tech to the warfighter is a national security imperative, which has led to greater willingness to work with companies outside the small suite of aerospace primes.
Few stories embody this incredible shift more than one that emerged in the middle of June: that of Mach Industries, and its 19-year-old founder Ethan Thornton. The company has captured interest from VCs and the DoD, landing Sequoia Capital’s first investment into defense tech and courting interest from the Pentagon. Mach’s seed round, which included participation from Marque VC and Champion Hill Ventures, came to $5.7 million.
Mach is developing hydrogen-powered platforms for the military, including unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), munitions and hydrogen generation systems. The company is betting that techniques like hydrogen combustion, powered by an energy source that can be manufactured in the field, will give the military an advantage in case conflicts with near-peer adversaries arise.
Speaking generally in a recent interview with TechCrunch, Thornton described a solution that’s less expensive, and perhaps less exquisite, than the ultra-costly weapons programs of today. It’s a mindset shift embodied in hardware: Instead of thinking in terms of missiles, think in terms of something more like bullets. On LinkedIn Thornton has said that the company is “working to replace gunpowder,” and in our interview he described a less expensive approach to munitions.
“Taking a missile [and turning it into] a bullet, every time you do that, you really, really decrease your costs,” he said. “That’s fundamentally one of the changes Mach wants to see happen: taking more away from the rocket equation — because you have to bring your own propellant, your own sensors, and things get very expensive — and back to actually an older model using more projectile-based systems.”
Thornton’s interest in hardware stretches back to his childhood; the way he tells it, it’s part-nature, part-nurture, with a grandfather who built kit aircraft in his spare time, a high school job as an auto mechanic and a small business selling handmade kitchen knives, cutting boards and other products.
At some point along the way, he developed what he called an “[obsession] with electrolysis.” Electrolysis is a process by which water is split into its constituent elements — one of which, of course, is hydrogen. The first result of that obsession was a small arms device he made while still in high school. The entire thing cost around $200 — funded by his parents, after he pitched them with a 20-page paper — and consisted of a couple of deer feeder batteries and an electrolyzer, all powering what was essentially a bazooka.
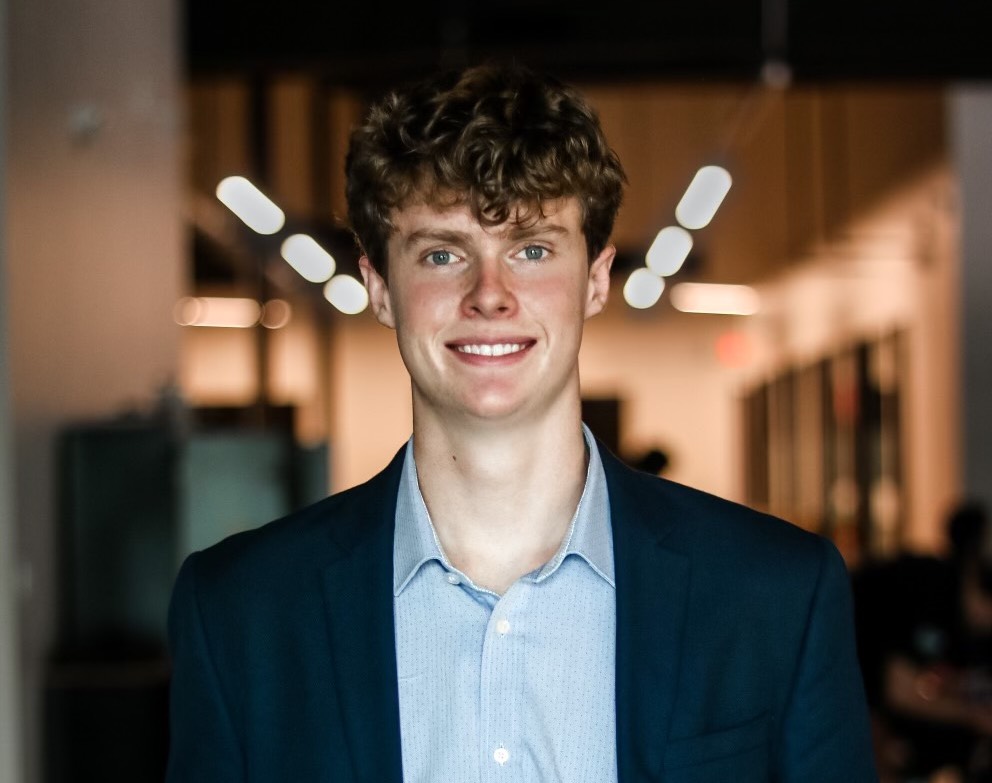

Mach Industries founder Ethan Thornton. Image Credits: Mach Industries
Before his first academic year at MIT even commenced, he started working with MIT Lincoln Laboratory, a national R&D center managed by the school for the DOD. The military has long had an interest in hydrogen, especially as a robust energy supply chain for contested war environments, and the lab had its own group focused on energy systems.
While Thornton realized that the Lincoln Lab wasn’t the perfect fit for what he wanted to build, he was able to build his government connections. And then he decided to drop out.
“This was pre-team, pre-revenue, anything,” he said. “I just couldn’t sit through classes anymore.”
Thornton also walked away from Lincoln Lab with two significant hires: Erik Limpaecher, who was a senior technical staff at the lab’s energy systems group, and who had been with the center for nearly 12 years; and Mark Donahue, a former program manager for control and autonomous systems, who departed the lab after 15 years. Limpaecher is now Mach’s chief innovation officer, while Donahue was installed as VP of engineering.
Thornton did end up finishing his first year at MIT this past spring, but not before putting together a team of undergrads and testing a large, mounted gun under the railroad tracks near Charles River, and joining the newest class of Peter Thiel’s Thiel Fellowship in February.
“I don’t like doing anything halfway, and I felt like I was doing college halfway, and [Mach] halfway. This was far and away the clear, no-brainer decision to make, and I haven’t regretted it.”
The Mach team, which is now about 15 people full-time, is headquartered in Austin but also maintains offices in Boston. There, the company conducts all the engineering work to build the systems; but Texas, with plentiful open land, is where the company actually puts the hydrogen to work in kinetic or combustible applications. It’s a split that has an almost eerie resonance with historical weapons development programs, with the brightest minds pulled from universities in the northeast and the product testing in the middle of nowhere.
For now, the company will use the seed funding to expand its engineering capabilities: manufacturing, R&D, and also to hire talent. Thornton hopes to be manufacturing thousands of products a year within the next five years, with certain systems in the hands of the end user within 12 months – though some, he said, will take more like 12 years.